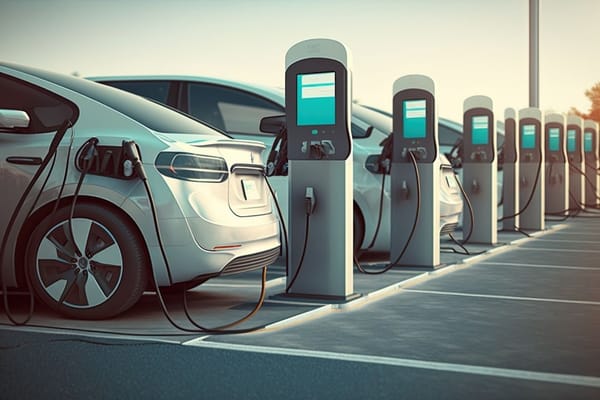
Wireless battery management system for electric vehicles.
The electric vehicle (EV) industry’s evolution to wireless battery management systems (wBMS) is inevitable. The benefits of wireless vs. wired BMS are crystal clear to anyone who’s grappled with the complexity,
In conventional Automotive Battery Monitoring Systems, measurements are carried out using wired solutions, and data interchange between the measuring unit and the central unit takes place using isolated CAN or isolated-SPI-based communication channels. This arrangement has drawbacks like considerable power dissipation, high cost, increased wiring harness complexity, and decreased accuracy.
The electric vehicle (EV) industry’s evolution to wireless battery management systems (wBMS) is inevitable. The benefits of wireless vs. wired BMS are crystal clear to anyone who’s grappled with the complexity, BOM cost, space, and labor penalties inherent to wired systems, no matter the application.
Wireless Battery Management System, in contrast, has shown promise in saving up to 90% of the wiring and up to 15% of the volume in battery packs for next-generation EVs. This is achieved by eliminating the communication wiring harness and connectors, leveraging instead of an intelligent battery module with fully integrated electronics—the only exposed connectors are the +ve and –ve terminals.
The benefits that come with wBMS technology can be realized only with huge investments in the design, validation, and manufacturing infrastructure needed to accommodate it. However, the security and safety requirements are unique to wireless systems and must reassessed from top to bottom at every stage of the battery pack life cycle, starting from manufacturing to reuse.
Benefits of wireless Battery Management Systems (wBMS)
- Battery assembly — the only connections a battery module requires are the power terminals, which can be readily made in a highly automated process. Eliminating manual labor for assembly and testing also avoids safety risks to assembly line workers. Furthermore, the modules can be tested and matched before installing inside the battery.
2. Servicing — secure wireless capability means the condition of the battery pack can be conveniently analyzed by diagnostics equipment in an authorized garage without touching the pack. A faulty module can easily be removed and replaced if a malfunction is detected. A wireless configuration simplifies the installation of a new module in the battery system.
3. Second life — to the increasing number of vehicles, a market is emerging for second-life batteries recovered from scrapped EVs and repurposed for applications such as renewable energy storage systems and electric power tools. This also creates a new source of value for EV manufacturers, which are responsible for recycling or disposing of the batteries in scrapped EVs since wBMS allows a simpler integration of the modules for second-life applications.
4. Disposal — the recyclable metal and potentially hazardous materials inside a battery pack require approved and regulated disposal arrangements. The simple connections and absence of a communications wiring harness make removing battery modules easier and quicker than a wired battery.
5. Data management — the wBMS technology makes it easy to read out critical battery data from each intelligent module: this means the condition of the batteries can be determined individually. These data can, for instance, provide information about the SOC and SOH of a module. Combined with data from when the module was originally produced, this allows optimal usage in its second-life application and the provision of a detailed set of specifications for each module on sale. The ready availability of these data increases the resale value of the modules.
Source:
i) Stephan Prufling (2023) What Are the Benefits of Wireless Battery Management Systems?




