Why is EV battery health important?
Lithium-ion battery is the most common type of battery used by most EV companies. The growth of lithium-ion is tremendous, their combination of performance,
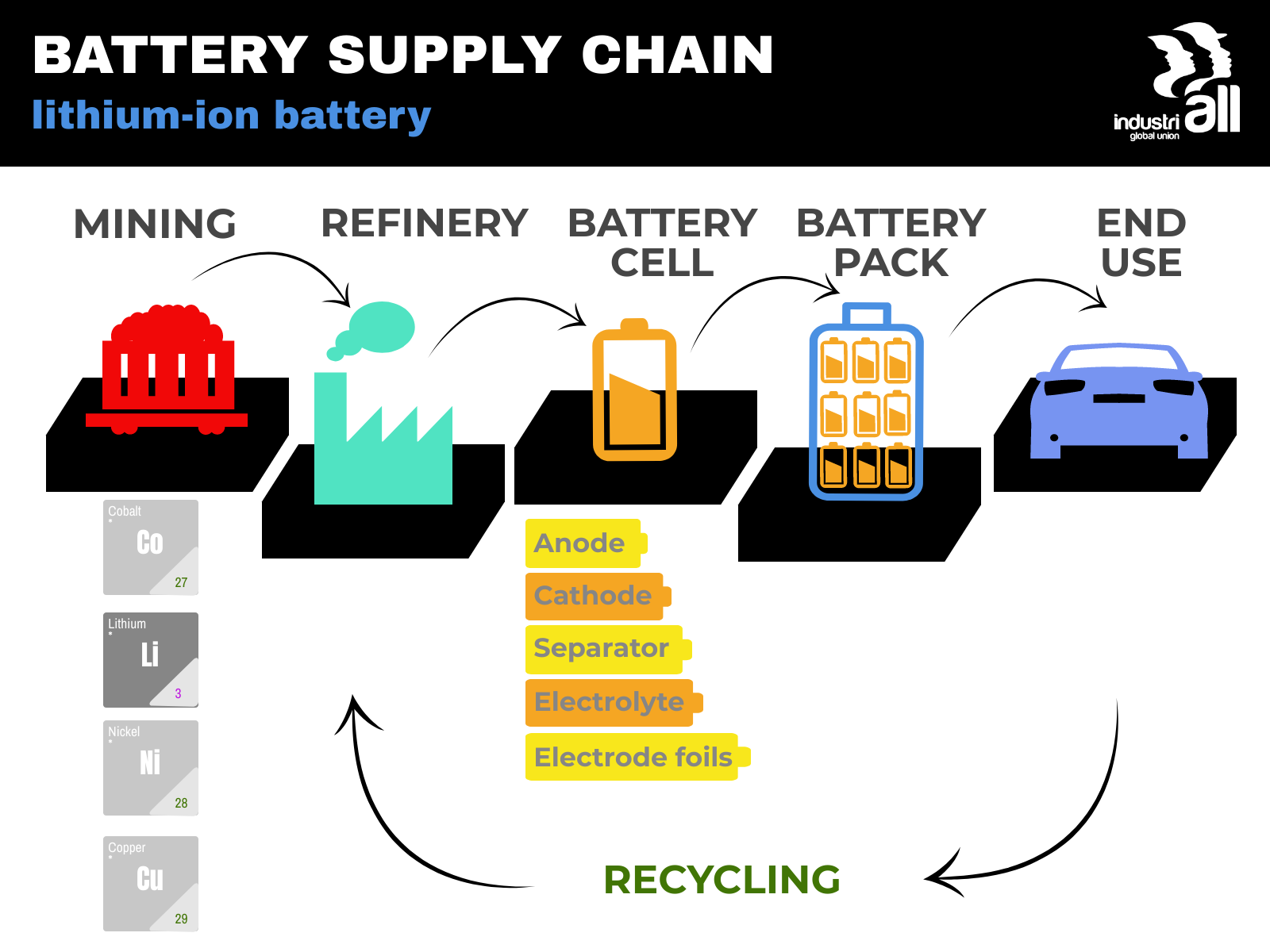
Lithium-ion battery is the most common type of battery used by most EV companies. The growth of lithium-ion is tremendous, their combination of performance, flexibility and decreasing costs makes them not only particularly suited for use in consumer electronics like smartphones and portable devices, but electric vehicles (EVs) as well.
It is easy to understand why electric car manufacturers choose to power their vehicles with Li-ion batteries. Because their energy density is much higher than, for example, lead-acid or nickel-cadmium rechargeable batteries, they can reduce the overall size of the battery pack and easily fit in in a normal-sized car. However, there are other factors to consider as well: in the automotive industry, safety is paramount.
Here’s what you need to know about EV battery health.
Factors affecting battery degradation
Lithium-ion battery is a low maintenance system: it does not require scheduled cycling to prolong its life, nor does it have the sulfating problem of lead acid batteries, which sometimes occurs when those are stored without periodic topping charge. And in case problems should occur, EVs are equipped with charging safeguards, ensuring the batteries are sufficiently protected during repeated charging sessions in a short period of time.
Still, repeatedly charging a battery is always going to cause degradation. High temperatures, operating at high and low state of charge and high electric current as well. As a result, the amount of energy the battery can store is reduced, as is the amount of power it can deliver. But because a Li-ion battery used in an EV is generally able to deliver more power than the car needs at any time, only the decreasing energy storage is of importance. It is also key to note that a decrease in storage capacity is not necessarily proportional to an EV’s action radius: factors like temperature, driving habits and cargo/passenger load also come into play here.
Lithium - ion batteries are not same.
Though generally designed to maintain optimal efficiency over at least 1000 full-charge cycles, most EV batteries last even longer. EV manufacturers offer warranties, which usually cover a certain amount of time and a certain number of kilometers' driven, and end when a threshold is met. These differ between manufacturers, and consumers are generally advised to study these closely.
Also, please note that not all batteries are the same. While research has shown that EV batteries generally decline non-linearly (an initial drop, followed by a more moderate decline and a significant drop at the end), depending on their make and model they respond differently to the test of time. The jury is still out on this one, but battery chemistry and thermal management are potential contributors to faster degradation.
Understand batteries better
In any case, having a monitoring and diagnostics solution with real-time statistics on battery health and performance helps prevent potential issues and to plan maintenance. It is important to have experts who will help explain to the customers more details about batteries . Details such as warranty are vital to the customers.
However there are some best practices that you can do to extend the life of your electric car battery.
If you have a heated garage then that's fine. If possible, keeping your car plugged in is good. This help to prevent overcharging and increase battery safety, and the EV itself will have on-board electronic protection, so you can rest assured that it will stay plugged in. The electric vehicle will use a small amount of power to keep the battery warm. This way, when you're ready to go, you won't experience a potential loss of energy by heating the battery. Many cars come with something called 'pre-conditioning'. You can set your departure time in the car's app, and for a short time before you leave, the car will electrically heat the interior to the desired temperature. This way, you don't need to start from cold on the road and the electricity you pull in comes from the grid, not your electric car battery. Driving in the best possible way can also be an important thing for battery life. This includes avoiding rapid acceleration and braking.
Finally, leaving your EV parked for too long with a full (or empty) battery can also cause battery degradation. To avoid this, if you are going to spend a significant amount of time away from your vehicle, it is recommended that you leave it fully charged to between 25% and 75%. There are smart charging stations that can help you do this and ensure that your battery does not exceed these limits.
Ref:
i) Akkurate (2022) WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW ABOUT EV BATTERY HEALTH




