Does A Self-charging Electric Car Exist?
Self-charging implies either some magical free energy from fairies which doesn’t exist or that the car can generate (utilize) some energy…


Self-charging implies either some magical free energy from fairies which doesn’t exist or that the car can generate (utilize) some energy it has onboard rather from an external source, like a charger.
The electric car needs the energy to move along. It has to get it from somewhere. Currently, that energy comes from the electricity grid or home solar panels, etc. It’s stored in the battery and discharged into the motors when you want them to propel the car along.
An attempt has been made to fabricate a self-charging battery electric vehicle which utilizes the rotational energy of wheels to charge the batteries, thereby introducing a system which makes the vehicle pollution free. The fabrication of chassis is made for the similar dimensions of commercially available golf carts in the market with some changes in its size and shape using C Channel type of Mild steel material. The components like alternator, motor and DC-DC converter was arranged in a manner to transfer the rotational energy being experienced by the MS bright rod to the alternator. The alternator here has the capacity to produce 12 V to 14 V, which is directed to DC-DC converter through a battery source. Here in DC-DC converter, the voltage source is stepped up to 54 V, which is enough to charge the 4 batteries in series which yields to 48 V usage. Thus the batteries which are used to provide the rotational energy to the shaft through a motor is receiving back the sufficient voltage source to recharge it. The vehicle is tested for the supply of source to the batteries using multi-meter, distance traveled with and without the recharging circuit is also studied and is found to be effective in its work.
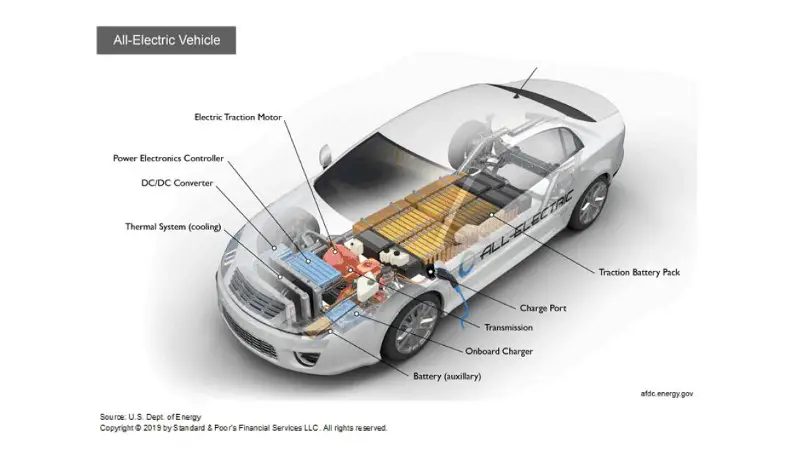
In operation, the Brushless DC hub motor is driven by a set of 4 drive batteries which are connected in series and provide an output voltage and current of 48 V and 28 Ah respectively which acts as the power train. The motor which is connected to the pulley through a belt drive system propels the vehicle and henceforth acts as a drive train. As the vehicle begins to move, the pulley keyed to rear axle connected to the alternator spindle through a belt begins to rotate, this, in turn, causes the alternator pulley to rotate, which disturbs the magnetic flux being produced thereby generating the voltage and current which is diverted towards a charging battery of 12 V, 7 Ah capacity. To this battery is connected a 12–54 V DC-DC converter whose function is to step up the 12 V from charging Battery to 48 V which is given to the set of 4 drive batteries which is connected to the motor




