
Charging an electric car is easy and can be done anywhere there is an outlet or charging station. Most EV owners charge their vehicle at home or at work. Public charging stations are also available at gas stations, parking lots, retail and grocery stores. All the equipment required to charge an electric car typically comes included. Typically this is an electrical cord which plugs into the vehicle and into a standard household power outlet. There are also a number of aftermarket solutions which can provide faster charging for electric vehicles.
EV charging levels
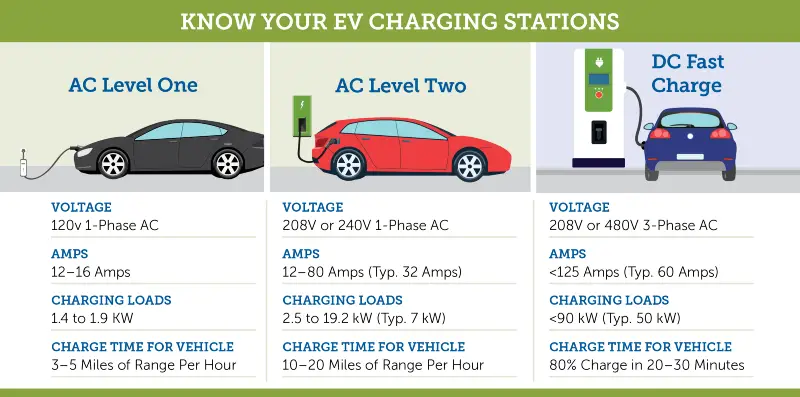
Electric vehicle service equipment (EVSE) is a term used for all EV charging solutions. EVSE solutions are further classified according to the rate (speed) at which they can recharge an EVs batteries. These are generally referred to as Level 1, 2 and 3 (or DC fast charge).
1. Level 1 charging (120v)
The easiest form of EV charging, level one uses a corded plug to connect to the vehicle to a standard household (120v) outlet.
- Lowest voltage and slowest form of EV charging.
- Can take over 8 hours to recharge a depleted battery.
- Typically used at home, when the vehicle is parked overnight.
2. Level 2 charging (240v)
Level two charging requires the installation of a specialized station which provides power at 220v or 240v and up to 30 amps. Typically level two stations are found at workplaces or at public charging locations. However, some homeowners may choose to install a level two station at home for quicker recharging times.
- Installation requires wiring and mounting of a charging ‘pylon’ and cord.
- Typically used for workplace public charging.
- It can take 4 hours to recharge a depleted battery.
3. Level 3 charging (480v)
Level three or DC fast charging is currently the fastest charging solution for electric vehicles. Unlike levels one and two, there is no standardized charging protocol for level three charging stations. Currently, the Tesla Supercharge Network, the Nissan CHAdeMO have deployed level three or high-voltage chargers. All of the above fast chargers deliver about 80% charge in 30 minutes.Installation requires wiring and mounting of a charging ‘pylon’ and cord. Because of the cost and power requirement of level 3 chargers, these stations are typically only installed along transit corridors.
- Can recharge a depleted battery in 30minutes or less.
- Typically only used in commercial applications.
How long does it take to charge an electric car?
Charging times for electric vehicles vary a great deal. Factors affecting the time required to charge include the total capacity of an EVs battery, the amount of charge required, and the charger level (or speed). While it is common to compare the times required to recharge the battery of an electric vehicle completely (from 0% to 100%) in practice, this is extremely rare. More commonly EV owners recharge their electric vehicles on a regular basis and seldom dip below 1/3 charge.
Average time spent charging per charger level:
- Level 1–290 minutes
- Level 2–115 minutes
- Level 3–23 minutes
Types of electric vehicle chargers
There are also two types of EV chargers, commonly referred to as ‘Smart’ or ‘Dumb’ chargers.
1. Dumb (Non-networked) EV charging stations
The biggest factors which affect the cost of an EV charging station are speed (charging level) and network capability. Chargers which aren’t connected via the internet to network management services are commonly referred to as ‘dumb’ chargers. Non-networked chargers are essentially a power cord plugged into an outlet. This form of charging is common in level one and level two chargers for home or commercial fleet use where the cost of charging stations is a consideration.
2. Smart (Networked) EV charging stations
Networked EV charging stations are more costly than non-networked options. Most EVSE manufacturers charge a premium for the collection of charging data. Networked charging stations also require a connection to the internet, either via WI-FI or cellular connection. For the cost of service, networked charging stations offer features such as the ability to delay charging remotely and monitor the energy use of charging.
Networked EV charging stations are typically operating at level two and three charging capacity. These are most commonly found in public charging locations where station operators may require EV owners subscribe or pay to use the station. A number of EVSE manufacturers offer ‘smart’ home-use charging stations.
Battery life or durability
The ‘life’ of an electric car battery depends on a number of factors which include:
i) Battery technology
ii) Total battery capacity
iii)Use of the battery
While consumers are not able to control factors related to battery technology and total capacity they are able to significantly increase or decrease the ‘life’ of a battery based on charging and usage habits. Electric vehicle batteries which are discharged completely will typically last between 300 to 500 cycles. The same batteries which are regularly discharged to only 50% capacity will see an increase of 3 to 4 times life expectancy.
How to increase the life of electric car batteries
- Avoid fully charging or discharging the battery.
- Avoid extreme temperature ranges, hot and cold.
- Use slow-charging, level one and level two.
Cost of electric car batteries
Electric car batteries are typically compared by looking at the at the cost per KwH, the total cost of the battery over the total electric capacity. While batteries continue to be a large proportion of the overall cost of a new electric vehicle, that ratio is changing. Recent battery technological developments, as well as consumer demand, is driving the price of batteries down substantially. Industry analysts are reporting that the cost of batteries is falling fast than expected. The cost of EV batteries has dropped 80% in the last 6 years to below $230/kWh. Forecasts project $100/kWh batteries by the year 2026.
How to increase electric vehicle range
1. Driving
- Maintain a regular/steady driving speed.
- Smooth/gradual acceleration and braking.
- Use of regenerative braking on equipped vehicles.
- Use of vehicles ‘eco’ settings.
2. Maintenance
- Ensure the vehicle is in prime operating condition.
- Ensuring tires are properly inflated.
- Remove unneeded heavy luggage or accessories.
- Pre-heating the vehicle before unplugging.
- Park in an enclosed or heated space.
3. Smart use of devices
- Use of heated seats over a heated cabin.
- Limit the use of air conditioning and heating.
- Limit the use of the stereo, electronics or high-volumes.




