Electric Car Battery Life Explained.
Electric vehicles use large batteries to store the electricity needed to power the motor(s). When those batteries' power is depleted, EV owners must stop to recharge before hitting the road again.
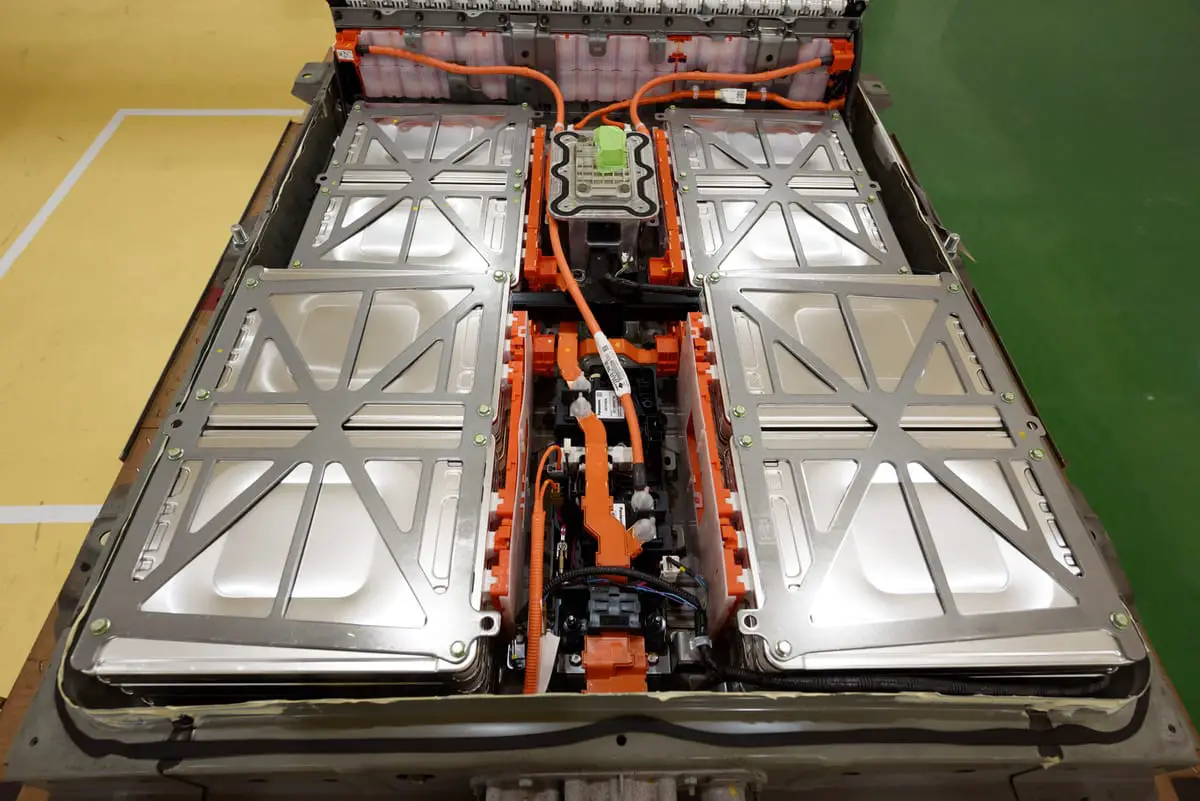
Electric vehicles use large batteries to store the electricity needed to power the motor(s). When those batteries' power is depleted, EV owners must stop to recharge before hitting the road again. Over time, all that charging and use can wear down a battery's ability to maintain capacity and capability. Different batteries wear at different rates, and driving habits have a big impact on longevity as well.
What are Electric Vehicle Batteries Made of?
Most electric vehicles contain lithium-ion batteries as they’re robust and relatively lightweight whilst still holding a lot of energy. Lithium-ion batteries were first developed for use in laptops and mobile phones and are still commonly used today. Most electric car batteries are comprised of elements such as metal oxide, lithium salt, and graphite or carbon.
Battery Degradation
Electric car batteries are just like the battery pack in cell phones or notebook computers in that they start to degrade over time and with use. Repeat discharge and charge, as well as thermal wear, can eventually reduce energy capacity and efficiency to a point that the battery is no longer able to provide decent range and charging performance. Most new EV models have special car battery technology and programming to prevent the battery from being completely discharged, which can help extend battery life and help the batteries maintain charging performance.
Depending on the car, operating in extreme temperatures can mimic true battery degradation. Hot and cold temperatures have similar effects on EV battery capacities by reducing range and slowing charging speeds. Beyond the obvious impact that temperatures have on the batteries themselves, the use of climate control systems and other electrical components can rapidly deplete battery power.
Preserve your electric car battery pack
To preserve your battery for a long there are a few things you need to do. Here are some of them:-
- Park away from extreme weather and temperatures, if possible. Some EVs operate temperature control systems even when parked, and we know that extreme temps can reduce battery performance. If you have the chance, park your EV somewhere out of the elements.
- Try not to leave the car plugged in to fully charge every time. Batteries are happiest in their "middle charge" state, and repeatedly operating at the top or bottom end of the charging spectrum can cause damage. This is especially true at the bottom end, where completely emptying the battery can cause problems with other vehicle systems.
- Watch your charging and discharge speeds. Using the fastest charger your car can handle isn't always the best idea, despite the convenience. Ramming as much power into your battery as fast as possible causes wear and tear, and can lead to premature failure. The same goes for discharge speeds. Repeatedly using launch controls or similar features drains the battery quickly and will eventually degrade performance and battery capacity.
How long do EV car batteries last?
Some electric vehicles last up to eight years or 100,000 miles. Some go above and beyond those numbers, but you can rest easy for at least eight years if you purchase a new EV. That's not to say that your battery will last that long, however, so it's not a guarantee that you'll have eight years of trouble-free operation. Some manufacturers' warranties carry stipulations on battery condition or operation before coverage is provided, so it's important to understand your car's warranty.
None of that tells us battery lifespan, however. In most cases, battery degradation happens slowly, with as little as a few percentage points of capacity every several years. Cars that operate primarily in extremely hot or cold conditions may see that decline happen much more quickly, but few people live at the far ends of the temperature spectrum without at least short periods of intermediate temperatures for relief. In most cases, electric car battery life expectancy should hit at least 100,000 miles before showing noticeable signs of degradation and should carry on to 200,000 or more if properly maintained.
Does EV charging affect the battery life?
Yes. Charging a battery does have an effect on your vehicle’s battery life.
One of the innovations that led to the rise of electric vehicles over the past decade is Lithium-ion batteries. Traditionally, most vehicle batteries were made from lead-acid and only had to start a vehicle’s motor with a short surge of power which would then be recharged as the vehicle drove by an onboard alternator. However, they were not ideal for discharging more than a few percent of their power and are often referred to as SLI batteries (starting, lighting, and ignition).
However, while an EV’s battery will lose its ability to fully charge over time, it is unlikely that it will stop altogether. There are a few best practices that you can do to extend the life of your EV’s battery.
EV battery charging best practices
The improvement over the past decades in lithium-ion batteries has been significant. The advances have extended battery life, increased safety, and reduced the weight and price of battery packs. However, like all pieces of technology, if you care for them in the right way, you can extend their longevity and increase your return on investment.
Are Electric Car Batteries Recycled?
80% of the materials in lithium-ion batteries are recyclable, so even when the electric battery comes to the end of its life, the raw components can be extracted and reused. Currently, the recycling process is difficult and long, but scientists are working to streamline this process so batteries can be recycled easily. At the moment, it’s estimated that 5% of lithium-ion batteries are recycled, but this will increase as technology advances.
Source:
i) Chris Teague (2022) Electric Car Battery Life Explained
ii) Wesley Van Barlingen and Callum Biggins (2022) How long do electric car batteries last?




