Are electric vehicles batteries all the same?
The batteries are essential for any electric vehicle because they power them. For all the electric vehicles it is the same with the same basic components. That is two electrodes, a cathode, and an anode.
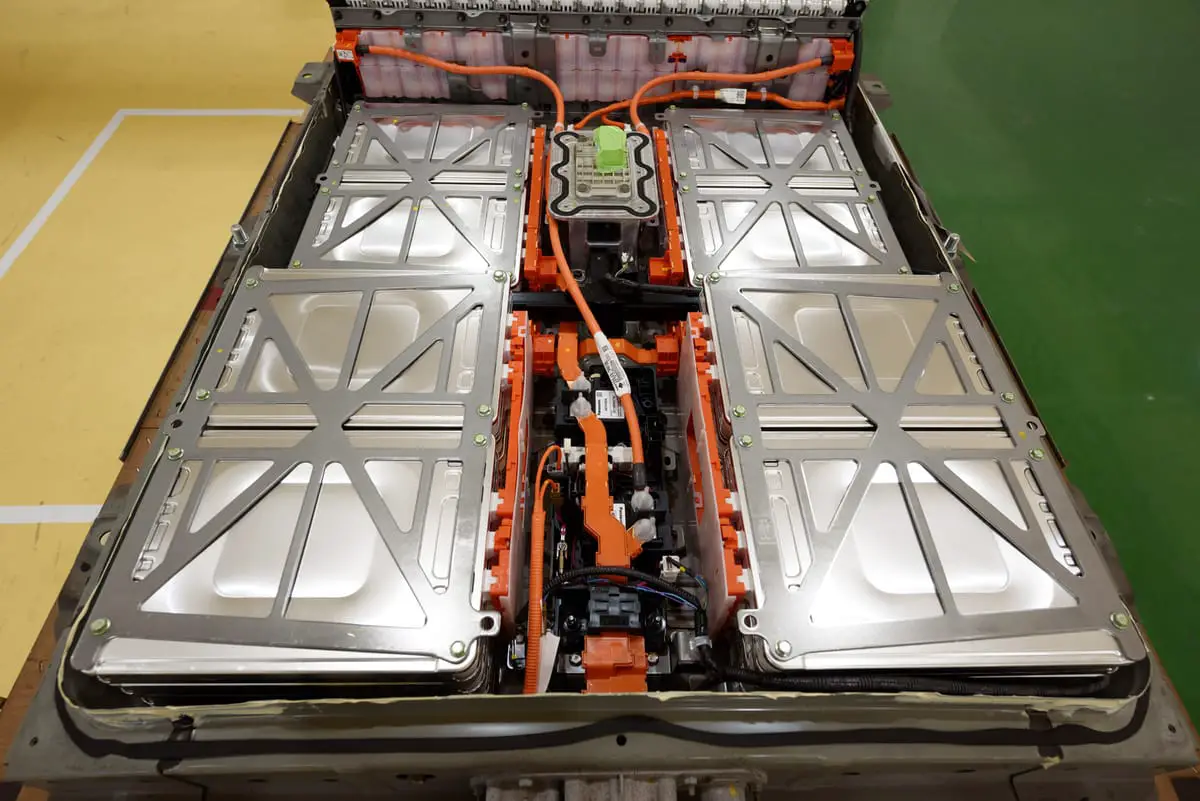

The batteries are essential for any electric vehicle because they power them. For all the electric vehicles it is the same with the same basic components. That is two electrodes, a cathode, and an anode.
An electrolyte helps shuttle the charge between them. But there are differences in the materials used, and that’s key to the amount of energy they hold. Grid-storage systems or vehicles traveling short distances can use cheaper and less powerful cathode chemistry that combines lithium, iron, and phosphate. For higher-performance vehicles, automakers favor more energy-dense materials, such as lithium-nickel-manganese-cobalt oxide or lithium-nickel-cobalt-aluminum oxide. Further refinements are seeking to improve range, how far a car can travel before recharging, as well as charging speed.
Charging your vehicle with electricity presents you with the opportunity to cut your greenhouse gas emissions by fueling your vehicle with a renewable resource like solar power. Averagely 80 percent of electric cars are charged at home. Additionally, many public chargers use solar panels to reduce the use of nonrenewable energy throughout the process.
At the beginning of 2000, Ni-MH batteries were the most advanced technology used in hybrid and electric vehicles. In comparison with the batteries used in those days, namely Ni-Cd and Lead-Acid batteries. Ni-MH technology was meeting the requirements imposed on batteries that were developed to be used in the automotive industry. The advantages were: high energy density and power, allowing autonomy of over 300 km while using batteries with 70 Wh/kg specific energy. Moreover, these batteries can be used with success in propulsion systems equipped with electric engines of 320 V AC, or 180 V DC, showing an increased lifecycle (until 80 % Depth of Discharge DOD).
Other advantages were: the capability of using regenerative energy recovered from braking, recyclable materials were used in their development, excellent thermal properties (operating temperature starting from – 30 °C up until + 70 °C), battery charging and discharging safety, etc. Between Li-Ion and NiMH batteries, Li-Ion cells offer specific energy increased by 20 %.

Types of electric car batteries
Lithium-ion batteries
It is the most common type of battery used in electric cars. You might have come across this kind of battery since it's used in portable electronics such as mobile phones and computers. Lithium-ion batteries have a high power-to-weight ratio, high energy efficiency, and good high-temperature performance. In practice, this means that the batteries hold a lot of energy for their weight, which is vital for electric cars – less weight means the car can travel further on a single charge. Lithium-ion batteries also have a low self-discharge rate, which means that they are better than other batteries at maintaining the ability to hold a full charge over time.
Additionally, most lithium-ion battery parts are recyclable making these batteries a good choice for the environmentally conscious. This battery is used in both AEVs and PHEVs, though the exact chemistry of these batteries varies from those found in consumer electronics.
Nickel-metal hydride batteries
Nickel-metal hydride batteries are more widely used in hybrid-electric vehicles but are also used successfully in some all-electric vehicles. Hybrid-electric vehicles do not derive power from an external plug-in source and instead rely on fuel to recharge the battery which excludes them from the definition of an electric car.
Nickel-metal hydride batteries have a longer life cycle than lithium-ion or lead-acid batteries. They are also safe and tolerant of abuse. The biggest issues with nickel-metal hydride batteries are their high cost, high self-discharge rate, and the fact that they generate significant heat at high temperatures. These issues make these batteries less effective for rechargeable electric vehicles, which is why they are primarily used in hybrid electric vehicles.
Lead-acid batteries
Lead-acid batteries are only currently being used in electric vehicles to supplement other battery loads. These batteries are high-powered, inexpensive, safe, and reliable, but their short calendar life and poor cold-temperature performance make them difficult to use in electric vehicles. There are high-power lead-acid batteries in development, but the batteries now are only used in commercial vehicles as secondary storage.
Ultracapacitors
Ultracapacitors are no batteries in the traditional sense. Instead, they store polarized liquid between an electrode and an electrolyte. As the liquid’s surface area increases, the capacity for energy storage also increases. Ultracapacitors, like lead-acid batteries, are primarily useful as secondary storage devices in electric vehicles because ultracapacitors help electrochemical batteries level their load. In addition, ultracapacitors can provide electric vehicles with extra power during acceleration and regenerative braking.
Source:
i) C Iclodean1, B Varga, N Burnete, D Cimerdean, B Jurchiș(2020) Comparison of Different Battery Types for Electric Vehicles
ii) EnergySage (2021) How do electric car batteries work?




