3 Eco-Friendly Options for Decomposing EV Batteries.
Electric vehicles are environmentally friendly and becoming more popular. However, retiring their batteries in an energy-efficient manner becomes critical to the future of our planet and its precious resources.
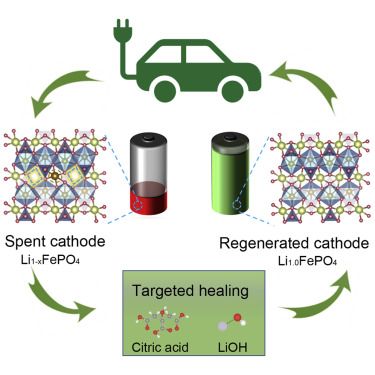
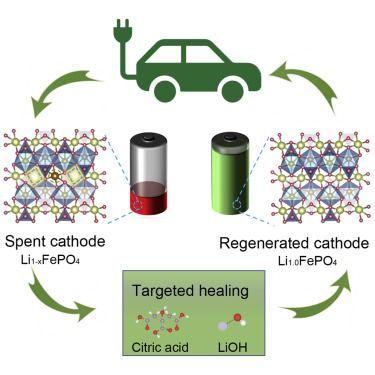
Electric vehicles are environmentally friendly and becoming more popular. However, retiring their batteries in an energy-efficient manner becomes critical to the future of our planet and its precious resources. Lithium-ion batteries, which are commonly used in EVs, can be hazardous to the environment if not properly disposed of.
Here are three eco-friendly ways to decompose them.
1. Battery Recycling
Recycling an EV battery is an eco-friendly option that will see a specialized company break down the battery into its component materials and use them to create new batteries or other products.
The most common lithium-ion battery recycling methods include:
- Hydrometallurgical recycling: This process is the most widely used around the world, and it involves using aqueous solutions (i.e., water and chemicals) to break down the battery and recover valuable materials, usually metals. These are then purified and used in new batteries or other products. The hydrometallurgical method is considered the most suitable for recycling spent lithium-ion batteries.
- Pyrometallurgical recycling: This process involves using high temperatures to break down the battery, and the resulting materials are then purified before they can be reused. The main advantages of pyrometallurgy are its simplicity and safety, but the high temperatures needed for this process require high energy input, produce high levels of greenhouse gas emissions, and yield a low recovery rate.
- Mechanical recycling: This recycling option recovers plastic waste through mechanical processes such as sorting, washing, drying, grinding, and compounding without significantly changing the material’s chemical structure. Mechanical recycling allows lithium-ion batteries to be reused multiple times, creating a closed loop and contributing to the circular economy.
2. Battery Reconditioning
Reconditioning is another sustainable option. This process involves restoring a partially degraded battery to its original state by replacing the cells and other components that have worn out over time or been damaged due to misuse. The resulting reconditioned batteries are tested, certified, and sold as second-hand products at a lower cost than new ones.
The benefit of this approach is that it prolongs the life span of EV batteries while also reducing waste and saving money compared to buying brand-new replacements. Reconditioning is best left to specialist companies with expertise in repairing lithium-ion batteries, although you could also attempt to do it in your own workshop. Only attempt this without specialist supervision if you're confident you know what you're doing—opening up an EV battery pack is relatively easy, but it can be dangerous.
Reconditioning is cheaper, faster, and less energy-intensive than traditional recycling methods. It also doesn’t require expensive equipment since most repairs involve simple tools, such as screwdrivers or pliers, which require minimal training before use. Overall, reconditioning is a cost-effective and eco-friendly option that can help extend the lifecycle of an EV battery while also reducing waste and saving money over time.
3. Battery Repurposing
Another eco-friendly option for retiring an electric car battery is repurposing it for second-life applications. EV batteries can still hold a significant amount of charge even after they are no longer useful for powering a vehicle. By finding another use for these batteries, they can continue to provide energy for other applications.
For example, retired EV batteries can be used for stationary energy storage, including in a home or business. They can, for instance, store excess solar energy during the day and provide power at night. Cells from repurposed batteries can also power electric forklifts or other equipment, reducing the need for new batteries and minimizing waste.
Several companies are developing second-life applications for retired EV batteries. For example, Nissan has several "second-life battery" initiatives for its LEAF electric vehicle, including installing second-life LEAF-sourced battery packs at its North American facilities and investigating new recycling methods. In 2021, Volkswagen Group also announced a battery recycling plant, as the automotive giant aims “to return valuable raw materials to the manufacturing process chain.”




